One of the most asked computing-related questions is: What are the differences between Computer Science, Information Systems and Information Technology?
The main differences are as follows:
- Computer Science (CS) focuses on Theory, Principles and Innovation on Application Technologies, Software Methods and Technologies, Systems Infrastructure. The practical component is low.
- Information Systems (IS) focuses on Application, Deployment and Configuration level on the area ‘Organisational Issues & Information Systems”. The theoretical component is low.
- Information Technology (IT) also focus on Application, Deployment and Configuration level but in different areas. The areas are Organisational Issues & Information Systems, Application Technologies, Software Methods and Technologies. The theoretical component is low.
Keep reading to find out more information that can help you understand which program is better for you.
Computing Curricula
The Computer Curricula report is a document created by a joint task force between scientific computing societies ACM and IEEE. The document shows recommendations for computing-related programmes.
The document has guidelines on all mayor computing-related subjects.
They also created other documents with specific recommendations on computing-related programs. They describe the knowledge areas and units, among a lot of other useful information.
There are several documents that you can check in this link, each dedicated to specific programs. So if you want to know more about the program you like, I strongly recommend you to check the respective document from the computer curricula recommendations.
As a word of caution, not every university follow these recommendations 100%. But most of the universities do follow them. So after reading the previous documents, you probably should also read the program published on the university website (the one you want to attend).
Computer Science
Computer scientists should be prepared to work in a broad range of positions involving tasks from theoretical work to software development
Computer Curricula
A Computer Science degree focuses more on theoretical aspects. It is perfect for innovators and creators in general.
You can get a strong foundation in several computing areas. It will enable you to have a broad and deep knowledge of computing. You will be able to move easily from an area of knowledge to another one during your career.
If you don’t feel comfortable in mathematics, then this degree is not for you; as mathematics is a fundamental part of the computing foundations.
See below a graphical view of computer science, according to the Computer Curricula.
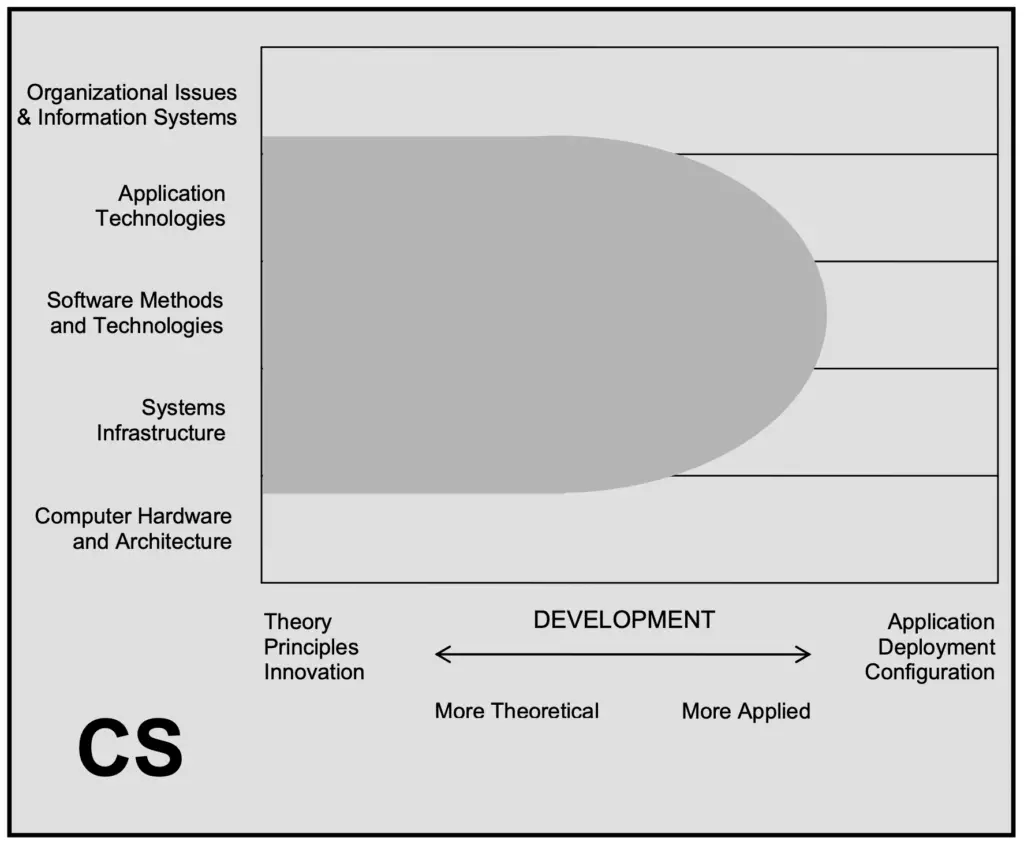
See below some of the career opportunities for CS graduates.
Carriers opportunities
- Data scientist
- Software developer
- Full-stack developer
- Software engineer
- Web developer
- Research positions
- Database designer/administrator
- Machine learning engineer
- Network architect
- Computer Science lecturer
Information Systems
Information Systems specialists should be able to analyze information requirements and business processes and be able specify and design systems that are aligned with organizational goals
When you study Information Systems, you study how to design, implement and work with software that its main function is to solve a business problem. For instance, accounting software, customer relationship management software, etc. We could say Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems in general.
IS study the processes that are carried on the organisation as well as ways of optimising them. Also, IS deals with the best way that information can be presented to the users.
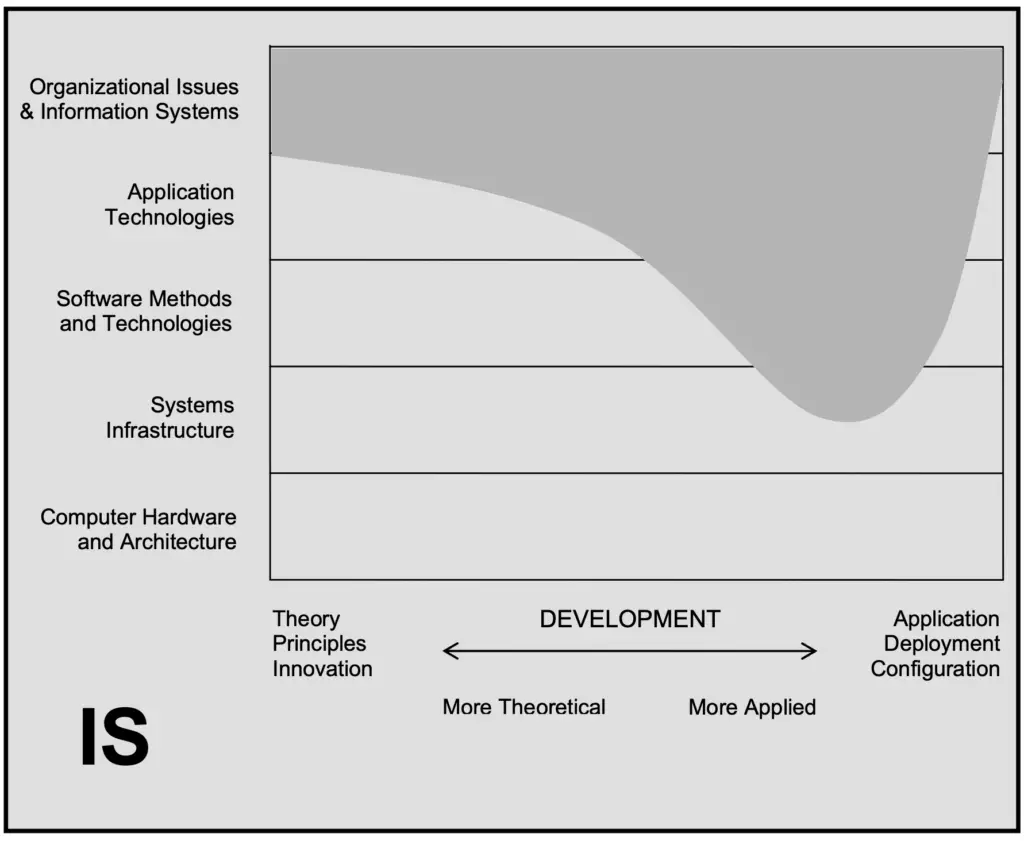
See below some of the possible employment positions for IS graduates.
Carriers opportunities
- Data analyst
- Software analyst
- System analyst
- Information architect
- Information system manager
- Software developer
- Database administrator
- Web developer
- IT lecturer
Information Technology
- “information technology professionals should be able to work effectively at planning, implementation, configuration, and maintenance of an organization’s computing infrastructure” Computer Curricula
If you get a degree in IT, you will have to do a lot of infrastructure support. Some of the most common roles for graduates from IT are Network administrator and System administrator.
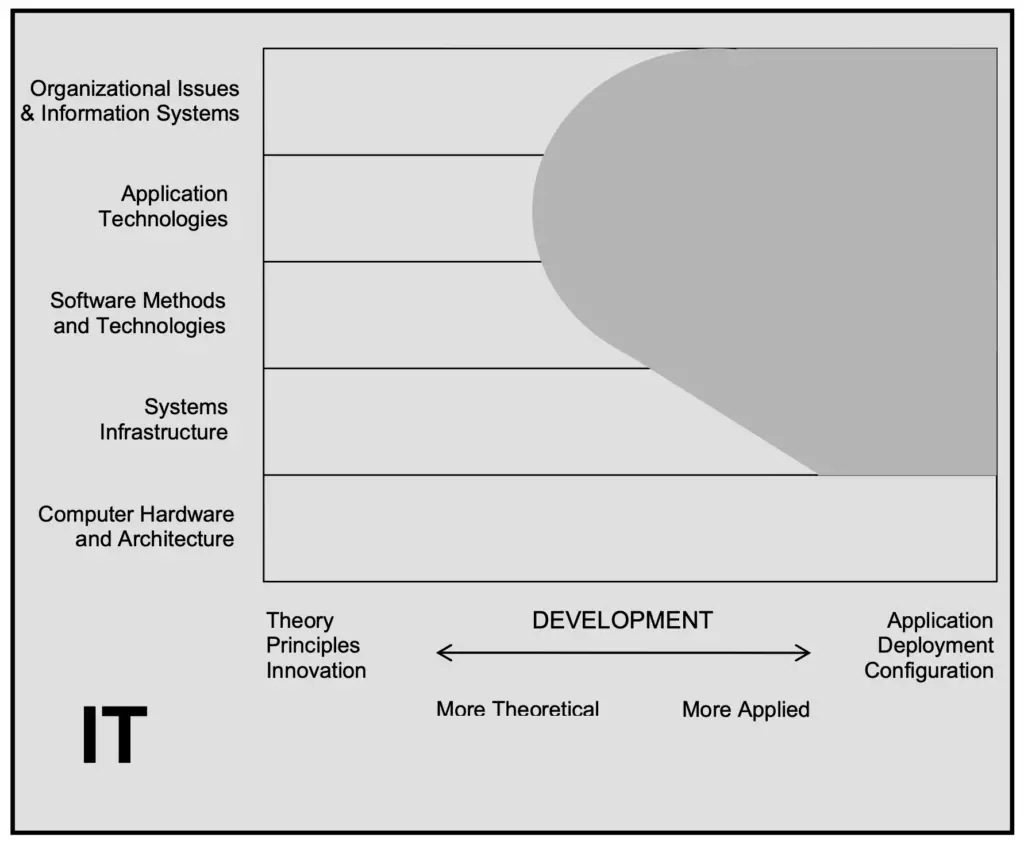
See below some of the possible positions for IT graduates.
Careers opportunities
- Network administrator
- Database administrator
- IT support analyst
- IT consultant
- IT Manager
- Cybersecurity specialist
- Data centre technician
- IT lecturer
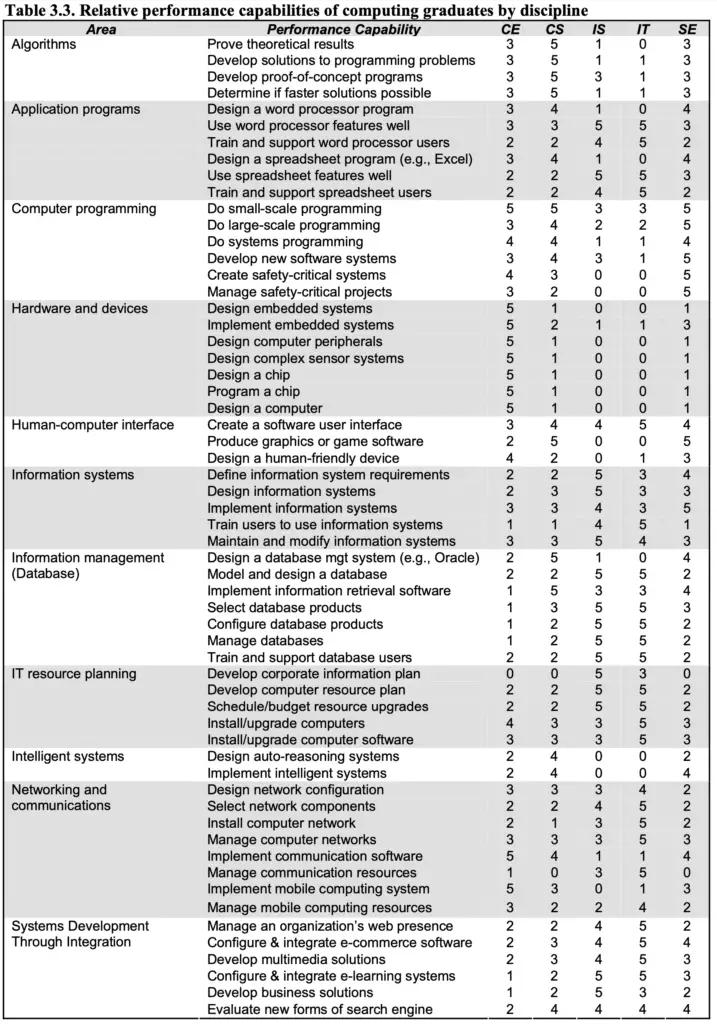
Graduates capabilities
There are certain expectations on the skills a graduate must have. The two tables below summarise the main capabilities that are expected from computing-related graduates.
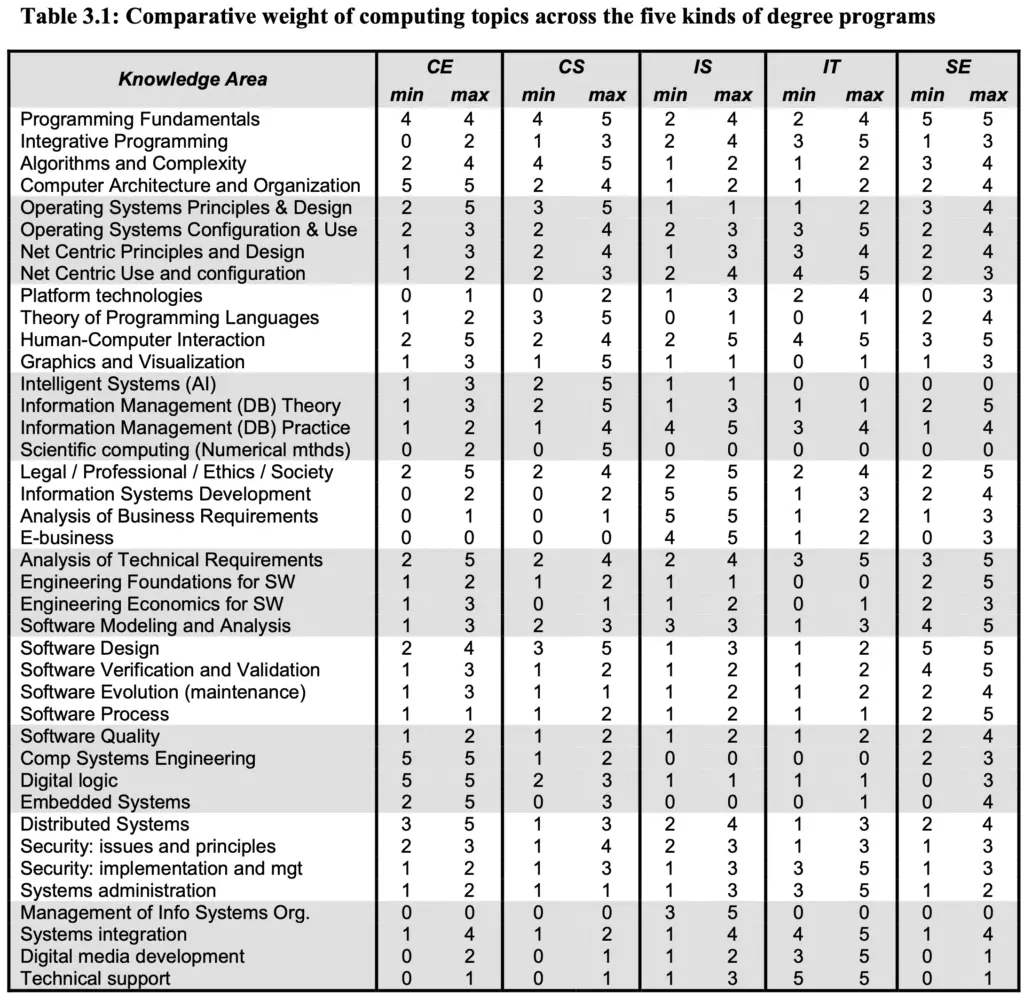
Summary
I discussed above the main differences between CS, IS and IT.
If you want to do a deep study of these differences, you should read the Computer Curricula recommendations.
The careers opportunities above, are not exhaustive. It is just a list of the common ones according to my experience.
If you have now a better understanding of the differences between CS, IS and IT, share the post so more people can benefit from it.
Good luck in getting your preferred degree!
